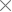Exploring the Materials and Structures of Protective Films
The aluminum protective film is a specific formula of polyethylene (PE) film as a substrate, polyacrylic acid (ester) resin as the primary material of the pressure-sensitive adhesive, coupled with several specific adhesive additives through the coating, cutting, packaging, and other processes, the protective film is soft, with good adhesive force, easy to paste, easy to peel. Pressure-sensitive adhesive stability is good and will not adversely affect the product's surface being pasted.
Scope of application: Mainly used for all kinds of plastic, wooden plate (sheet) surface protection, such as PVC, PET, PC, PMMA two-color plate, foam board UV board, glass, and other plate surfaces in the transportation, storage, and processing, installation process without damage.
Structure and material properties of protective film
The protective film is generally polyacrylate protective film, polyacrylate protective film of the basic structure from top to bottom: isolation layer, printing layer, film, adhesive layer.

(1, isolation layer; 2, printing layer; 3, film; 4, adhesive layer)
1. Film
As raw materials, film is generally made of low-density polyethylene (PE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Extrusion molding, injection molding, and blow molding can be obtained. As polyethylene is cheaper and more environmentally friendly, 90% of the film is made of polyethylene, with the blow molding process as the main focus. There are many types of polyethylene with different melting points and densities.
2. Colloid
The characteristics of the colloid determine the key to the good and bad of the protective film. The protective film used in pressure-sensitive adhesive has two kinds: solvent-based polyacrylate adhesive and water-soluble polyacrylate adhesive; they have different characteristics.
Solvent-based polyacrylate adhesive
Solvent-based polyacrylate adhesive is an organic solvent as a medium to dissolve the acrylic monomer; the colloid is very transparent, the initial viscosity is relatively low, and very resistant to aging for up to 10 years when exposed to ultraviolet light; the colloid will also be slowly cured. After the film is corona-treated, polyacrylate adhesive can be directly coated without primer. Polyacrylate adhesive is more complex and has poor fluidity, so the protective film adhesion plays more slowly; even after pressure, the gel and the surface to be posted still can not be fully contacted. Placed 30 ~ 60 days later, it will be fully in contact with the surface to be posted so as to achieve the final adhesion, and the final adhesion tends to be greater than the adhesion of the adhesion of 2 ~ 3 times, the adhesion of the protective film, if suitable for the board factory cutting, the end-user tearing the film when there is It may be very laborious or even can't be torn off.
Water-soluble polyacrylate adhesive
Water-soluble polyacrylate adhesive uses water as a medium to dissolve the acrylic monomer. It also has the characteristics of solvent-based polyacrylate adhesive, but the colloid should be avoided to reduce contact with water vapor and prevent residual glue. Developing countries often use the colloid to produce protective film because the water-soluble polyacrylate adhesive is more environmentally friendly and does not need solvent recovery devices.

3. The characteristics of the colloid
Adhesion
Refers to a period when the protective film from the surface is affixed to the force required to peel. The adhesion force is related to the material to be applied, pressure, time of application, angle, and temperature when peeling off the film. According to Coating Online, generally, with the rise of time and pressure, the adhesion force will also rise; the protective film adhesion can rise too much to ensure no residual adhesive when tearing the film. Typically, the adhesion is gauged through a 180-degree peeling test.
Cohesion
Refers to the strength of the colloid inside, as a protective film of the colloid cohesion must be very high; otherwise, in tearing the protective film, the colloid will be cracked inside, resulting in residual adhesive. Measurement of cohesion: The protective film will be affixed to the stainless steel surface, and a specific weight will be hanging on the protective film to measure how much time is needed to pull off the protective film by the weight. If the adhesive force is greater than the cohesive force, tear off the protective film, and the adhesive molecules connected between the bond will be broken, resulting in residual adhesive.
Adhesion
This refers to the bonding force between the adhesive and the film. If the adhesion force is greater than the cohesion force, if the protective film is removed, the bond between the adhesive molecules and the film will be broken, resulting in residual adhesive.
UV Resistance
Polyacrylate adhesive is UV resistant, transparent polyacrylate adhesive protective film with a UV stabilizer; it is UV resistant for up to 3 ~ 6 months. General use of climate simulation equipment to test the UV strength of the protective film by adjusting the temperature radiation intensity, and condensation to mimic climate change every 3 hours of high humidity and 7 hours of ultraviolet radiation for a cycle of 50 hours cycle of experiments is equivalent to the equivalent of about one-month outdoor placement.


 Inquiry
Inquiry Whatsapp
Whatsapp Email
Email